Automated Guided Cart - AGC - The low cost AGV
This article explains into detail what is an automated guided cart (or underide), what are different kinds of Automatic Guided Carts, what are the main applications of agv transfer carts, how do AGCs work and it shows main advantages and disadvantages of Under ride AGVs.
AGCs are flexible, low cost, easy to install and could represent a key factor to cut logistics non value added tasks.
Let's discover Automated Guided Carts.
What is an Automatic Guided Cart?

An automated guided cart is a mobile robot characterized by small chassis and low profile that engage carts or shelves underneath.
Depending on the navigation technologie, AGCs could be both:
- Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) if they perform line following navigation (magnetic, etc)
- Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) if they perform natural navigation methods.
Keep on reading, we'll see this point into detail in the navigation chapter.
What is the difference between AGV vs AGC?
Nothing... Automated Guided Carts are a type of Automated Guided Vehicle. Nothing else.
While the load remains on the AGC, Automatic Guided Carts are also called Underide, Platform, Lurking AGV , Mouse AGV, Under Cart AGV , AGV transfer cart or Tunnel Type Automated Guided Vehicles.

Do not miss agvnetwork's ebook with all mian articles of this web. It's FREE and you can download it here.
| Click here to download the ebook |
|
Table of contents:
Automated Guided Carts features What are AGCs navigation methods? What kind of batteries mount Automated Guided Carts? What are the main Automatic Guided Carts applications? How do Automated Guided Carts move? Automated Guided Carts Advantages Automated Guided Carts Disadvantages Automated Guided Carts Manufacturers - Discover main AGC manufacturers close to your facilities |
In the following TABS you can find some of the best and most reliable AGC Manufacturers Worlwide. You are welcome to contact them to BOOST your logistics.
Types of Automated Guided Carts
There is not any official AGC classification. We could distinguish AGCs depending on the way they engage the load:
AGCs with pin hook
This kind of AGC counts on pin hooks (one or two) that engage the cart. In this case, it is mandatory to have a platform, cart or trolley with wheels.
The cart must be adapted to be consistent with the AGC hook and shape.
When the AGC engages the load, AGC pulls it and the load weight is supported by the cart's wheels. In this case, in order to have good cart manoeuvrability it is desirable to have all swivel wheels in the cart.
In general, this is the cheapest type of AGV because these vehicles use to perform magnetic or optical line navigation (so the most basic navigation technology).
Moreover, considering that the load is supported by the cart, the AGV chassis and motorization are lighter allowing good towing rates with limited power.
AGCs with lifting device
In this case, the mobile robot lifts all the load (cart, shelf, box, pallet, etc). It is not mandatory to the load to be equipped with wheels because the load weight is supported by the AGV itself.
This kind of mobile robots or platforms perform more advance natural navigation and they are not obliged to follow a given line. In this case, these robots are known as Autonomous Mobile Robots.
These vehicles are gaining more and more applications, for example, they are widely used as autonomous mobile robots in warehouses, for goods-to-person applications improving pickers productivity.
In fact, the main amazon warehouse robots are low profile vehicles transporting shelves to picker stations.
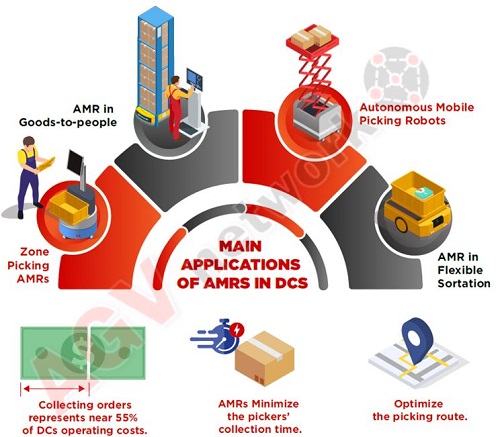
Infografic: Mobile Robots in e-commerce
| Click here to download the infographic |
Automated Guided Carts features
What is maximum load capacity of an AGC?
AGCs are typically 0.5 ton capacity (near 1.100 lbs), even if we can find vehicles reaching 3-ton (6.600 lbs) and more.
What is maximum AGC speed?
I general, the maximum speed is 40 m/min (130 ft/min – 1570 inch/min) or 60 m/min (195 ft/min) for AGCs with line following line navigation (so AGVs).
Natural Navigation (AMRs) are able to run up to 120 m/min ( 390 ft/min)
What are Automatic Guided Carts dimensions?
The AGC must be able to go under a cart or a shelf, in this case the key dimension is the “height”. Low profile AGCs allow to work with more kinds of carts or require less modifications on carts.
Let’s say that smaller it is, better it is. Of course, AGCs with bigger dimensions can hold higher loads or bigger batteries.
The heigth of the standard AGVs is around 300 mm (1 ft / 12 inch). The height is given by the AGC components such safety scanner, motors, wheels, batteries, etc.
We can find some lower AGCs, only 6,7 inch (170 mm) high.
Regarding length and width, it depends on the AGC manoeuvrability and travel direction of the AGC. There is not any standard.
What are the typical AGC navigation methods?
As anticipated above, the automated guided carts or platforms can perform different types of navigation.
- If they perform line following navigation (magnetic, etc) thay are under the AGV umbrella.
- If they perform natural navigation methods they are considered as AMRs.
I will not get too much into detail about the different navigation technologies, if you would like to know more, I suggest you to read this article: AGV Navigation Technologies.
Of course, do not foget to download the free whitepaper explaining the main differences between agvs and amrs.

| Click here to download the whitepaper |
Line following technologies are considered “old fashion” but they are very reliable and vehicles are really competitive price-wise.
On the other hand, more and more AGV manufacturers are proposing “free or natural navigation” using different natural agv navigation. These technologies do not require any infrastructure (like the magnetic tape) allowing complex circuits and manoeuvres.
Free navigation is the future and it will substitute any other AGC's navigation methods soon. Free navigation is improving and becoming more convenient day after day.
What kind of batteries mount Automated Guided Carts?

There is no one single answer. The kind of batteries depends on the whole project rather than the vehicle itself. The project performance and feasibility will determine the recharging strategy and consequently will define the battery type.
Battery management is a complex matter, these two articles explain better what are different possibilities for battery management and battery selection.
Types of batteries for AGV and AMR
Battery management systems for AGV
The type of battery depends on the recharging strategy:
- If we have battery swap, AGCs are supplied with sealed GEL batteries with no emissions and no maintenance required. If the AGC is properly designed, 100Ah GEL battery can last even 16 hours before it is necessary to change it.
- AGCs can also perform online or opportunity charging. In this case it is advisable to have a battery able to support short and intensive battery recharging, for example with Pure-Lead batteries or Lithium batteries.
In any case, the trend sees more and more applications with Lithium batteries.
What are the main applications of the Automatic Guided Carts ?
AGCs can be used everywhere. Here you have some of the main applications of AGCs:
- Healthcare & Hospitals
Underide or AGCs are widely used as Hospital AGV. They are used to transport:
Meals from the kitchen to wards and the return of empty trays to the kitchen.
Waste bins and trolleys. Full and empties management.
Linen transportation (clean and soiled).
Deliver trolleys/carts for cleaning and activate cart-washing systems.
Sterile Supplies Transportation.
Drugs and other supplies in the hospital (wards, theaters, pharmacies, laboratories etc).
- Ecommerce and Warehousing
Low profile vehicles are one of the most important types of warehouse robots. As explained above, small Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) platfrms are widely used as G2P Robots in Ecommerce.
Rather than having an operator walking along infinite corridors while looking for material in a warehouse (wasted time and energy), the material and goods come to the operator thanks to Goods To Person Robots.
There’s increasing demand of warehouse robots able to move racks in ecommerce distribution centres. These AGCs lifts racks and serve picking docks for ecommerce delivery.
There are several types of Warehouse Automation Solutions boosting material handling applications, do not miss agvnetwork's with tons of info about warehouse robotics topic.

Do not miss agvnetwork free guide with useful info and illustrations
| Download The Warehouse Automation Guide |
- Industry applications
Components supply to assembly/production lines and finished goods removal from the end of the line
This is one of the main applications. AGCs are one of the best solutions for this task because they can leave and pick-up material autonomously without any human intervention.
In the example below, the human operator is taking parts from the end of the line and putting them into a box situated in a cart.

1) Operator is filling the box located in “B” while the “A” position is free. AGV is arriving with an empty box.
2) The AGV deposits the cart+ empty box in “A” and waits for the “OK” to pickup box in “B” once the operator has filled the box in "B". The “OK” can arrive to the AGV Management System in different ways: push button from the operator, MES info, PLC line, etc. While waiting for the “OK”, the AGV could perform on-line charging, for example.
3) The AGV goes to “B” to pick up the full box
4) The AGV picks up full box from “B” and goes to the warehouse
In this sequence the operator does not move any container or box and he only dedicates to production. Moreover, if there’s space enough for AGV manoeuvre, the operator only must turn 90° to keep on placing parts in the box, so a very good result from the ergonomics point of view.
Of course, there are many types of lines and the space available is not always the same. AGC manoeuvres and footprint will depend on its cinematic. See point below.
Flexible assembly lines
AGCs can be used as flexible production or assembly lines themselves offering huge advantages: path flexibility, scalability, product customization, assembly line relocation, informatic intelligence integration, etc.
Do not miss this article it you wish to know more about the advantages of assembly lines “made of” AGVs: Assembly line AGVs .
How do Automated Guided Carts move?
There are several types of AGCs depending on the cinematic of the vehicle.
Unidirectional AGCs

These are the simplest AGVs, they only go forward, so they only can work in a loop circuit. Of course, they are limited but also less expensive. Do you know how much does an AGC cost? You can discover it in this article: AGV cost estimation. How much does an automated guided vehicle cost?
Bidirectional AGCs

AGCs can move forward and backwards. These AGCs are more complex while they need “two” heads with two laser scanners. These AGCs can be used when there is not possibility to complete a loop, when it is necessary to go into a closed production area with no possibility to go forward, etc.
Bidirectional – Differential - Rotational

AGCs can rotate on their central axis. These AGVs are more flexible because the have zero turning radius and can perform movements in very tight spaces.
The counterpart is that they should be in the centre of the trolley so if trolley is too big there could be some issue to access to AGV control panel or emergency push button.

Rotational capacity also depends on the cart dimension. The leverage force needed to rotate a big cart is much higher than the leverage force needed for a small one.
Omnidirectional Automated guided Cart

Omnidirectional AGVs can travel in any direction. There are several kinds of wheels that allow this movement, the most important are mecanum wheels. Check this video from KUKA AGV.
Regardless the type of wheels, the most important thing is that SAFETY SCANNER must cover 360° around the AGV .
Omnidirectional AGCs uses to have some kind of lifting table instead of the pin hooks to allow laser scanners to work properly below the wheel height once the load has been lifted.
Here below a “rough” representation of an omnidirectional AGC without lifting that is moving a cart.
AGC needs four laser scanners to grant safety areas in every direction, of course, there will be some “blind” area depending on the cart size.

Here below an “always rough” representation of AGC that lifts the load and covers 360° with only two safety scanners. As you can see, when the AGC lifts the load, the safety laser beam remains below the wheels so there is not beam interruption.

One of the main concerns of people approaching the agvs for the very first time is: “Are AGVs safe?”. In this article, you can discover further about the AGV safety standards and devices that we can find in an AGV in order to make it safe and reliable.
Or, again, you could download agvnetwork's whitepaper fully dedicated to the mobile robot safety topic.... really nice !

| Click here to download the whitepaper |
What are the advantages of the Automated Guided Carts?
- AGCs use to be less expensive than other types of automated guided vehicles such forklift AGVs or Tugger AGVs.
- AGCs transport material safely because the whole load width in travel direction is covered by safety laser beam
- Possibility to engage/disengage the load autonomously without human intervention
- Minimal footprint impact, allowing complex manoeuvres in tight spaces
What are the disadvantaes to AGCs?
- Transport capacity is limited because they use to transport only one load unit. Other AGV types, like tugger agvs or unit load agvs are able to transport several units in one single mission
- Speed is limited compared with other AGVs such forked agvs with laser navigation method
- It could be necessary to adapt carts or shelves, what means additional costs
Automated Guided Carts Manufacturers
In these tabs you can find some of the main AGC suppliers.
Here you can download the complete list of AGV manufacturers worldwide
DOWNLOAD THE AGV MANUFACTURERS EXCEL LIST
|
Related articles
11 Advantages of Automated Guided Vehicles
AGV vs AMR. What's the best?
AGV Market Size - How big is the AGV Market? |
 Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Follow me on LinkedIn... let's create a mobile robot community to discuss and learn about these outstanding systems.



