What can Warehouse AGV do? Types and Tasks
 Warehouse automated guided vehicles are here and here to stay. They are overcoming traditional manned vehicles in many industries and specific applications such as ecommerce and distribution centres.
Warehouse automated guided vehicles are here and here to stay. They are overcoming traditional manned vehicles in many industries and specific applications such as ecommerce and distribution centres.
There are some warehouse tasks where agv robots are simply the best and provide excellent economic results. It is not a secret that mobile robots are becoming a crucial resource to reach a decent level of warehouse automation.
This article will drive you through the different types or warehouse agv systems with special regard to their applications.

Types of warehouse automated guided vehicles (agv)
There are several types of warehouse agvs depending on the specific application.
Warehouse agvs are simply awesome, they can perform many different tasks from sorting small parcels to racking heavy pallets at 12 m high.
Check this article: Warehouse Automation Companies
We can classify them into two main groups:
✅ Forked AGVs: Typically Laser Guided Forklifts (LGVs) for pallet handling operations.
✅ Small Autonomous warehouse robots used in distribution and fulfillment centres for goods-to person, picking, sorting, etc.

There is a clear distiction between AMRs and Automated Guided Vehicles.
This article focus es on Forked AGVs applications in warehouses, if you wish to learn more about autonomous mobile robots in warehouses instead, I suggest this article: AMR Warehouse : The Distribution Center Revolution.
AMRs are an evolved type of AGV… so an AGV with specific features such Natural Navigation or the capability to “decide” a path. In fact, this is the main difference between agvs and amrs.
Do not forget to download the my free Whitepaper explaining the differences bewteen AGVs and AMRs.

| Click here to download the whitepaper |
AGV forklifts are one of the most effective cutting-edge tools available to boost productivity and improve safety in warehouses needing pallet handling operations.
Self-driving forklifts can accurately detect shelf slots, read barcodes, and detect pallet jack openings while improving warehouse safety conditions.

As you need to expand your existing warehouse or build a new one to support your growth, you will need to decide what type of pallet handling system you need to install.
|
Let’s discover how do warehouse agvs improve warehouse productivity |
Automated Guided Vehicles used in a warehouse automation for pallet handling
AGVs are a powerful tool to optimize your warehouse operations. AGVs offer many benefits like increase inventory accuracy and avoid mistakes.
Nevertheless, the physical environment and proper management are the two major challenges when it comes to deploying an AGV solution in warehouse and distribution facilities.
Integrating AGV to work within your specific storage system, your inventory method, and your specific application requires in-depth understanding and careful design.
There are several types of AGVs, typically laser guided vehicles (LGVs) that can be used in warehouses for pallet storage.
Each one has its own specifications, so each of them is more suitable for certain types of storage methods.
a) Pallet jack and Stackers
The AGV pallet jack is ideal for floor-to-floor operations or for operations requiring maximum 3 m stocking height. Regarding payload, typically, pallet jacks handle around 1 ton (2.200 lbs.).
Here you have some examples of automated pallet movers. Visit the AGV Network Showroom.
✋???? To be honest, there are more and more pallet jacks and stackers using Autonomous Navigation rather than traditional Laser Guided Navigation.
b) Counterbalance AGV Forklift Truck
These vehicles are very versatile. They can be configured to handle heavy payloads, even 4 ton (8.800 lbs.), or high stocking operations around 8 meters (26 ft).
Click here to discover more about Kollmorgen solutions for AGV'S and Mobile Robots
c) Reach Truck AGV
Robotic Reach Trucks are a kind of forklift designed for reaching objects from high shelves in a narrow space. Their turning radius is around 3 m (10 ft.) which is sensibly lower than the standard forklift trucks.
d) Very Narrow Aisle AGV Trucks
Click here to discover more about Kollmorgen solutions for AGV'S and Mobile Robots
Very narrow aisle AGV are used when you need high-density storage. Thanks to these AGVs you can increase the capacity of the warehouse without expanding the space because they can handle racks with narrow aisles of around 1,7 m (5,5 ft.).
The following table shows some typical specifications of AGV Forklifts used in warehouses.
FORKLIFT AGV TYPE PALLET MOVER COUNTERBALANCE OUTRIGGER REACH TRUCK VNA VEHICLE EXAMPLE ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Racking Warehouse MINIMUM AISLE WIDTH (Distance between pallets) 3,6 m/140'/11,8ft 4,5m/177'/14,7 ft 3,7m/145'/12,1 ft 3m/118'/9,84ft 1,6m/ 63' / 5,3 ft MAX SPEED FORWARD 2 m/s - 386 ft/min 2 m/s - 386 ft/min 2 m/s - 386 ft/min 2 m/s - 386 ft/min 2 m/s - 386 ft/min LOAD STORAGE HEIGHT 1,5 m / 60' /4,9 ft 9 m /354 '/ 29,5 ft 4 m / 157'/ 13 ft 9 m /354 '/ 29,5 ft 11 m / 430' / 36 ft MAX LOAD CAPACITY 1.500 kg /3.300 lbs 2.500 kg / 5.500 lbs 1.500 kg /3.300 lbs 1.500 kg /3.300 lbs 1.200 kg / 2.645 lbs VEHICLE PRICE $60.000 $85.000-
$120.000$85.000-
$120.000$120.000-
$150.000$150.000 - $200.00
What pallet storage methods can be performed by AGVs in warehouses?
- Pallet racking
- Gravity racking
- Mobile racking
- Drive-in racking
- Block stacking
a) AGV for Pallet Racking

Pallet racking is the most common type of storage rack used in warehouses.
Pallet racking can be used in small warehouses and in large logistics centers. Unlike other racking systems, pallet racking is characterized by reduced initial investment and operating costs.
AGVs can manage racks , but there are a few things to take into account while designing Racks for AGV applications.
Unit load Sideway and above tolerance
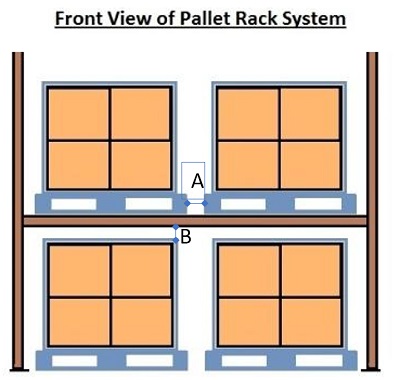
Standard tolerances pallet racking for fluent load handing are:
A: Distance between pallets: 3 inch (75 mm)
B: Distance between load top and beam above: minimum 3,9 inch (100 mm)
Usually racking operations are managed by counterbalanced or reach truck AGVs because they do not need supports beneath the forks so the floor can be used for stocking material.
If the rack allows to introduce support legs, in some cases, it is possible to use AGVs such as pallet stackers or pallet jacks.
Distance between pallets one behind the other back-to-back
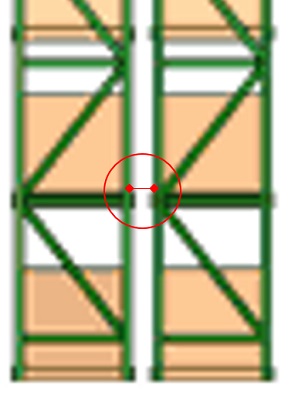
Minimum distance needed is 3,9 inch (100 mm)
b) Gravity Racking
Gravity flow racking is used to store products quickly on a roller conveyor. Gravity racking hasn’t aisles, so racks are utilized efficiently without waste of space.

Gravity racking is more expensive than standard racking, but its ROI is fast because they save space, time, and labor.
Gravity racking is the best option for first-in, first-out (FIFO) management because the goods are moved to the loading location by gravity.
Gravity racks can be managed by AGV forklifts, but there are some important things to take into consideration.
- Do your pallets have enough big pockets for forks or do you need a tilting mast?
- What is the needed side and vertical tolerance?
- Does your AGV have support legs or should the AGV be counterbalanced?
Gravity racks are inclined so the space for the forks is vertically limited. In other words, a gravity rack must have fork pockets or the forks mounted in the AGV must be able to tilt. Of course, tilting forks are more expensive.
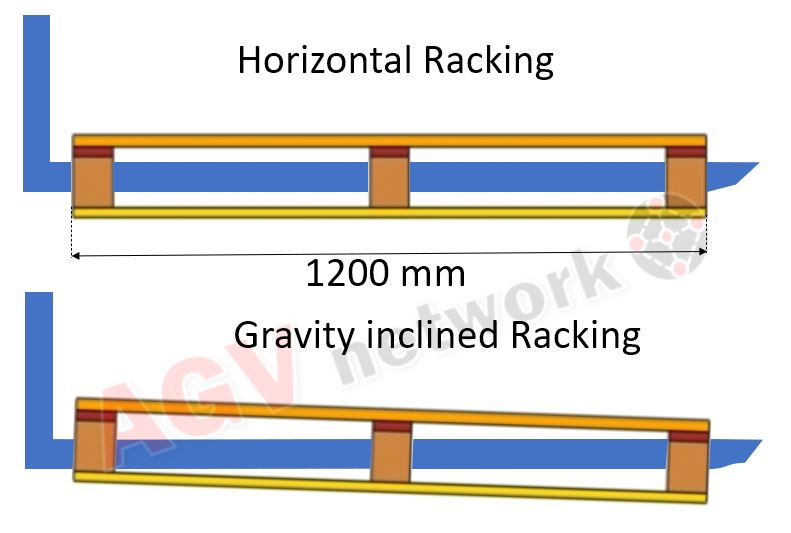
Regarding side tolerance and vertical tolerances, they are the same as what’s needed for the standard racking 3 inch (75 mm) lateral and 3,9 inch (100 mm) vertical to the next rack beam.
c) Mobile Racking
The mobile system consists of a common pallet rack mounted on a mobile platform. The shelves move on rails, so aisles are opened or as required.
AGV Forklifts can communicate with the WMS and mobile rack plc to coordinate the aisles opening/closing. It is important as well to have established communication protocol (via OPC, TCP/IP, I/O, etc.) to ensure the AGV moves into the aisle when is completely open and that the aisles are closed when the AGV is out from them.
The type of AGV forklift will depend on the aisle width, storage heigh and payload. So, we could have VNAs, Reach Trucks or counterbalance forklifts.
Another important topic in regards to the mobile rack stopping accuracy is that it should be done in +/- 3 cm (1,2 inch).
Racking operations are commonly performed by Laser Guided AGV (regardless of the vehicle shape).
Mobile racks count on many moving pillars. Laser Guided Vehicles need fixed reflectors to navigate, so for this reason it could be necessary to leave a “navigation window” in the height of 2m/3m (6-10 ft) to allow the laser beam pass through this window to find fix reflectors installed in the AGV working area.
d) Drive-in Racking
The main advantage of drive-in racking is the high density of rack storage due to the elimination of aisles between rows. Drive-in racking is particularly advantageous in warehouses where storage space costs are very high.
Drive-in racking is the best solution for storing large quantities of similar products or products with low turnover.
The best solution for drive-in racking is counterbalance AGV forklifts.
e) Block Stacking

Block stacking refers to unit loads stacked on top of each other and stored on the warehouse floor in lanes or blocks. The pallets are retrieved from the block in a last in, first out (LIFO) manner.

Compared to other racking methods, block stacking is cheaper to implement because it does not require racks and can be operated anywhere as long as open space is available.
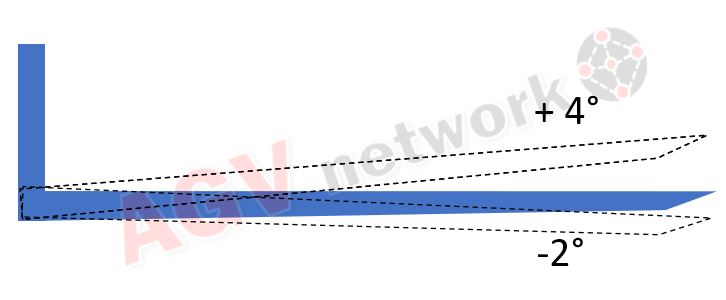
AGV Forklifts can perform block stacking, but the load must be stable and its top surface must be as flat as possible with an inclination lower than 3°.
It is also important that the support surface area does not go down or sink at a lower height. If this happens, the theorical height to stack a block is not real, so it is necessary to include sensors such as a “pallet finder.”
AGVs are fine, but the Management Software is the key.
Mobile Robots vehicles are effective and nice. Different brand may even look similar. However, they have different technical characteristics based on the specific several supplier features.
What really makes the difference is the robotic supplier capacity to manage information and provide optimized routing and order management.
You could have the best mechanical AMR on earth but if you are not able to optimize workflow your system will not be worth its price.

A good Management Software will lead to excellence.
AMR&AGV solutions are complex systems rather than a collection of simple commodity equipment.
Each mobile robot fleet arrive with its own MES/WMS systems as a core solution.
The software manages the location of shelves that store SKUs, it manages the quantity of SKUs stored, and it manages the order requirement to SKUs.
Based on these data points, the system can coordinate and guide the robot where to pick up the goods, and where to transport these goods. It virtually manages the entire order fulfillment process.
When an order is placed by a customer, it will be processed by the WMS system.
The data is then transferred to the Robot Control System, which will send the location of the stock to the AMRS over a wireless network.
In most cases, the robot software needs to integrate with customer’s management systems, which can be done using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
Many platforms integrate automatically with major WMS packages, including Manhattan, JDA, HighJump, SAP.
Tracking data is essential to determine fulfilment and warehouse performance.
For this reason, Management Software integrates reporting tools and performance dashboards that provide operations reviews, inventory management and slotting, and volume and future growth planning. All of this is critical to a successful warehouse management.
The information and data are displayed in fancy interfaces with useful graphs and tables. You can find tons of info such as:
- Daily view of volume, including hourly pick data
- Monthly view displays daily and monthly volume data
- Daily Performance indicates associate daily performance data
- Robot Map shows the current robot locations and status
- Pick Map displays the current robot, associate, and pick locations
- Open Work Heat Map lets you see how “hot” each location is related to open picks
- Associate & Bot Rates show current rates for robots & associates, including historical rates
- Robot Charging Info displays the robots that are charging and robot charging levels
|
Related articles
Autonomous Forklift Manufacturers List AGV Forklift Price - The key factors you should know Warehouse Drones Inspections – The era of autonomous inventory count VNA AGV - List of Manufacturers and Characteristics of Very Narrow Aisle Robots |
 Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Follow me on LinkedIn... let's create a mobile robot community to discuss and learn about these outstanding systems.







