The AMR Robot Guide - Discover Efficient Autonomous Mobile Robots
 In this article I explain the main aspects related to Autonomous Mobile Robots: What are AMRs? Where are them used? How do AMRs work? What are pros and cons?
In this article I explain the main aspects related to Autonomous Mobile Robots: What are AMRs? Where are them used? How do AMRs work? What are pros and cons?
I've been selling and deploying mobile robots for a while (near 10 years ... 😬), and I can honestly say that some years ago I had many concerns about them .... but now, amr robotics are becoming better day after day (even if I still find AGVs more interesting or convenient for some applications).
 My name is Alfredo Pastor... I've sold and deployed autonomous mobile robots from different suppliers and this is my experience with these amazing vehicles.
My name is Alfredo Pastor... I've sold and deployed autonomous mobile robots from different suppliers and this is my experience with these amazing vehicles.
AMR robots are proliferating in numerous industries because they are becoming more and more reliable, user friendly and affordable.
There is still much work to be done, but as autonomous technology advances, AMRs will overcome every challenge. Let me explain you what autonomous mobile robots are.
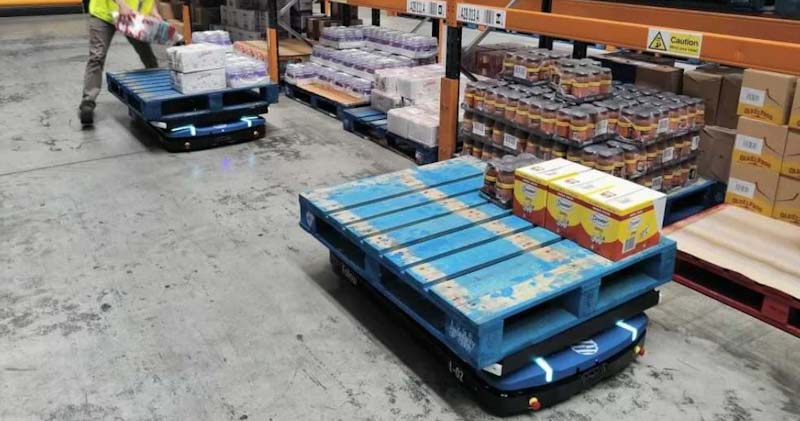

What is an Autonomous Mobile Robot AMR?
Simply put, Autonomous Mobile Robots are PLC or PC controlled robotic vehicles that navigate autonomously without need of tapes or reflectors and that are able o avoid obstacles.
Mobile Robots use a complex array of sensors, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and computing for path planning to interpret and move around their environment.
Here you have some examples of AMRs:
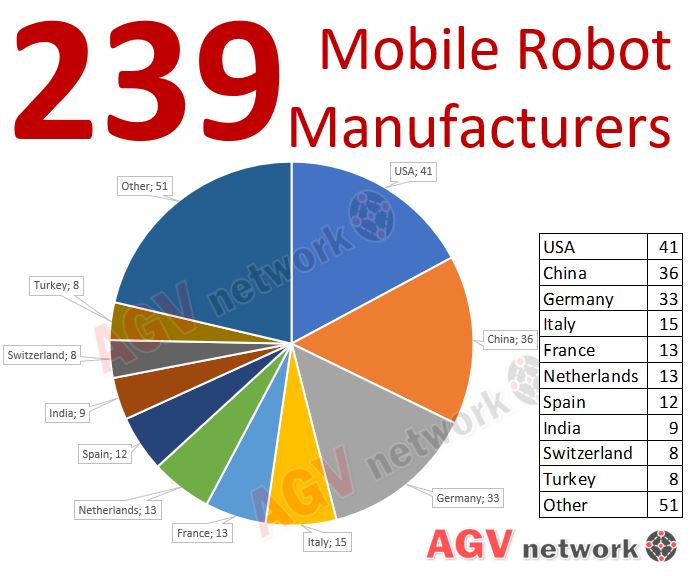
Difference between AGV and AMR?
💡 Pay attention... there are two main concepts that make the difference compared to AGVs : MOBILE AND AUTONOMOUS.
✅ Autonomous Seamless Navigation - No need of given track (like magnetic or laser triangulation).
✅ Ability to avoid obstacles - Mobile
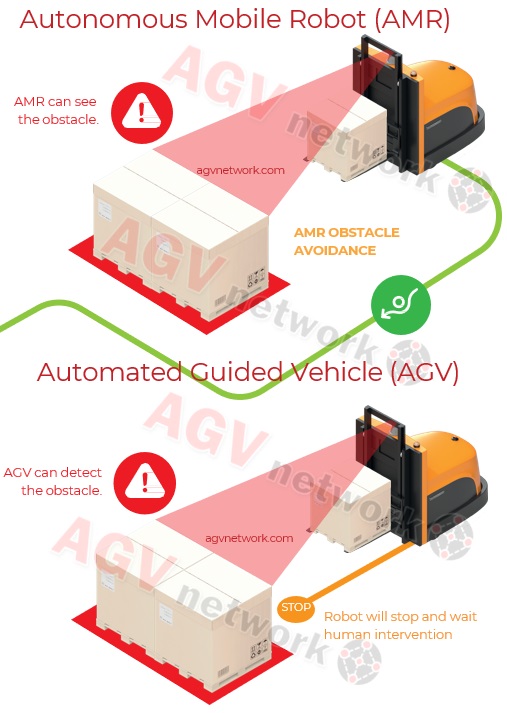
Thanks to this cutting-edge technology, if AMRs come across an unexpected obstacle while navigating, like a fallen box or a crowd of people, they will use collision avoidance systems to slow down, stop, or reroute their path around the object and then carry out the rest of their task.
There are some other differences between agvs and amrs related to reliability, accuracy, applications etc.
If you wish to know further, I suggest you to download the my whitepaper where I explain the main differences between AGVs and AMRs into detail.
🙋🏼♂️ My thought: Please take note that I do not advocate for any particular technology; instead, in the whitepaper I offer my unbiased view and highlight the benefits and drawbacks of each solution.

| Click here to download the whitepaper |
Of course, AMRs open new applications that AGVs could not perform in the past.
For example, could you imagine an automatic floor cleaning machine or a security robot following a magnetic tape? Simply put... it would not be possible.
So, let's discover something more about the autonomous mobile robots and... please... 🙏🏽 share this article if you're enjoying it
Are you still paying attention?? Great, we have just started 👇, let's go ahead.
How do Autonomous Mobile Robots Work?
Autonomous mobile robots move through a facility along a pre-planned course, stopping occasionally to carry out pre-programmed tasks.
|
Let's make it easy, this is how typically AMRs work: ✅ The robot is guided manually or remotely along the path that we wish to perform ✅ While running, the robot maps the environment (walls, columns, etc) and record a route ✅ So we have a route and a map ✅ Then it's time to work autonomously. ✅ The AMR navigates autonomously following that route and checks/verifes the surroundings to make sure that what it "sees" matches the map so: it is where it was supposed to be |
Where are Autonomous Mobile Robots Used?
AMRs can be used everywhere. AMRs are mainly suitable for applications having multiple and variable destinations where the "free" navigation and autonomous skills make the difference.
AMRs are widely used in ecommerce, hospitals, grocery, pharma, for access to dangerous areas without guiding infrastructure (fire, nuclear, military applications), etc.
🙋🏼♂️ I have to admit that AMRs are step by step entering in the manufacturing industry replacing AGVs in many applications.
If you want to know the key appplications where AMRs are breaking the rules... do not miss this article: Key Applications of Autonomous Mobile Robots
How do Autonomous Mobile Robots Navigate?
This is one of the main features: AMRs perform “free” or Natural Navigation, so navigation without need of hardware such wires, tapes, reflectors, QR codes, etc.
|
It means that the AMR is not “bonded” to any physical guide or object. |
Before having Natural Navigation, we only had Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
AGVs navigate performing different navigation technologies, for instance, using a laser navigation system to triangulate position and movement or following a magnetic tape on the floor.
These old technologies need some kind of hardware in the working area to enable localization and navigation of the robots.
Autonomous Mobile Robots instead, do not need anything to navigate because they can, for example, identify and map the surrounding area. They “see” walls, columns, shelves... they can localize and navigate with this info.
One of the main concepts is called SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping). SLAM is a set of algorithms used to navigate. As implied by its name, the robot maps its surroundings and locates itself on the map.

There are several technologies and sensors to map and track the environment and estimate AMR positioning. Each AMR manufacturer uses one of these technologies or a combination of the following ones, for example:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) scanners (they could be 2D or 3D)
- 2D or 3D cameras (Vision Navigation)
- Sonar, Radar
- Ultra-wide band sensors (UWB)
- GPS
- IMU, Encoders, etc.
In general, in order to have a more accurate navigation, AMRs navigate with a combination of these sensors, this is called Sensor Fusion.
|
🙋🏼♂️ My takeaway: "There is not a best navigation technology, there is a best navigation supplier" |

As you can imagine, Natural or Autonomous Navigation is becoming very important in the mobile robot industry, do not miss this article to have a better understanding about this amazing technology: Natural Navigation AGV
Why are AMRs "Autonomous"?
Autonomus Means that the robot is free to deviate from a predetermined path. An autonomous mobile robot has the ability to redefine routes and choose the optimum track to reach a specific location.
The AMR "decides" the best route after "looking" at its surroundings. AMRs provide the option of effortless and simple route changes.
If you want to change the magnetic route of an AGV, it is very easy but it would require some more job.
If you wish to add a new picking or delivery location or alter existing LGV route... You'd likely be unable to accomplish anything on your own and would need your supplier's complete support. 🤷🏽♂️
Due to their tremendous flexibility, AMRs may easily add many destinations and tracks during their implementation.
The AMRs can bypass obstructions thanks to their "decision capacity," which allows them to continue moving without having to wait the obstacle to be removed.

Example of LGV triangulating with reflectors positioning: Fixed path from A to B

In the pictures above, a Laser Guided Vehicle with reflector laser triangulation detects an obstacle with its safety scanner and stops. It only can follow the pre-programmed route from A to B.

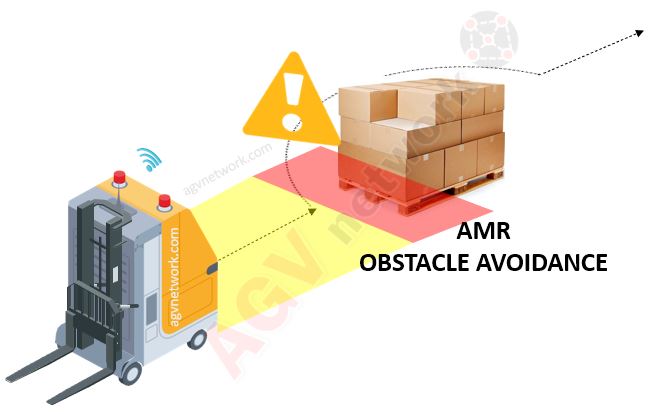
In these other pictures instead, an AMR, that is mapping all the enviroment (red walls), detects and obstacle with its safety scanner and can decide an alternative route to avoid it and reach B.
Of course, an AMR can recalculate its guidepath or not. You can choose how to behave. It depends on the supplier and on the project itself. Sometimes it is not worthy to leave this freedom to the robot.
In general, what type of vehicle is an AMR?
As previously said, an AMR is more the result of navigation technology and its behaviour rather than a particular kind of vehicle. In fact, an AMR Robor could be a forklift, a platform, a towing tractor, etc.
- Automated Guided Carts or platforms. Many under ride AMRs are low profile vehicles useful for moving carts or shelves.
- Autonomous Forklifts are light vehicles suitable for moving pallets from floor to floor.
- Autonomous Tow Tractors. More and more tow tractors are adopting the autonomous navigation, specially for Outdoor AGV Systems .
![]()
💡 These vehicles are just an example, for more detailed info, check my article: 14 types of Autonomous Mobile Robots
How much does a mobile robot amr cost?
On average a mobile robot platform costs near $32000-$40000. Of course, this value by itself does not mean anything. Apologize.🤷🏽♂️
Regarding autonomous tow tractors, the cost is near $40000 for max towing capacity of near 3 ton. If you increase capacity to 8 ton you can expect to pay near $70000.
If we talk about forklifts, price range could vary from $45.000 to $200.000. Of course, a pallet jack will be cheaper than a reach truck.
Check this article wehere I provide more details about autonomous forklifts price: Invest or Not? Decoding Autonomous Forklift Costs

What are the AMR Safety Standards?
 The are three main safety standards:
The are three main safety standards:
In the US, we mainly have:
- part 1 defines the safety requirements for Industrial Mobile Robots (IMR) and their attachments (rollers, manipulators, etc).
- part 2, published in 2023, specifies requirements for integrating, configuring, and customizing an IMR or fleet of IMRs into a site.
In the EU and Globally, we have the
✅ ISO 3691-4:2023. This Type-C International standard specifies the safety requirements for driverless industrial vehicles, AGVs and AMRs.
Of course, beyond these specific standards, there are many other rules and procedures to know/understand like the ISO12100, B11, etc.
Do not miss this article with more information about the different standards used for mobile robots: AGV and AMR Standards
|
🙋🏼♂️ My takeaway: Although these standards aren't compulsory for manufacturers, it's vital for you to understand them. Ensure your supplier adheres to these standards. |
What are the Advantages of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)?
-
Installing mobile robots is simple.
-
Installation is fast.
-
Installation cost is low.
- You can easily modify routes.
-
Nothing intrusive is installed in the working area.
-
No external infrastructure is needed for natural navigation.
-
No expenses for implementation and maintenance.
What are the Autonomous Mobile Robots Disadvantages
- Natural Navigation is "sensible". Due to the unpredictable surroundings in industrial settings, robots may experience navigational issues. Here it comes the manufacturer capability.
-
AMR vehicles cost more than AGVs because of more sophisticated algorithms and better sensors that must be included in order to have a reliable and efficient free navigation system. On the other hand, AMrs will require fewer expenses for implementation and maintenance.
-
Less accurate location and positioning compared to agvs using other navigation techniques. For instance, AMRs could not store materials on shelves that are more than 10 meters high since doing so needs highly precise tolerances, which are challenging to achieve using natural navigation technology. Here it comes the manufacturer capability.... again.
Conclusions
Mobile robots are cool...😎.
They are becoming more reliable, efficient, and affordable. But remember, every robot is unique, armed with proprietary algorithms and solutions that define its capabilities.
So, it's essential to choose wisely, focusing on the robot's capabilities rather than flashy branding or latest cutting-edge technology.
It's clear that each mobile robot represents a new adventure, and I, for one, can't wait to see where this roller coaster ride takes us.
|
Related Content Autonomous Mobile Robots Applications - 7 Key Uses Natural Navigation Automated Guided Vehicles What is Warehouse Automation? Is it for you? The Must-Read Ultimate Guide Autonomous Mobile Robots used in Warehouses Automated Guided Vehicle Robot? All the answers in one shot |
Follow me on LinkedIn... let's create a mobile robot community to discuss and learn about these outstanding systems. Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).