AMR Interoperability: Maximizing potential for the future
To be genuinely useful and efficient, a mobile robot must be able to connect with and work with a wide range of other devices. Welcome to the interoperability world!.
Because of its capacity to automate and streamline processes, increase productivity, and decrease costs, mobile robots have seen widespread adoption across a variety of industries.
There are three main aspects involved in interoperability:
✅ Ability to integrate AMRs with external Systems
✅ Ability to interact with human-involved processes
✅ Heterogeneous AMR fleet operation
Let’s discover them one by one ????
Ability to integrate AMRs with external Systems
When it comes to realizing the full potential of autonomous mobile robots, system integration is key.
IoT devices, lifts, scanners, conveyor belts, sorting machines, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and warehouse management systems are just some of the many possible integration points for AMRs.
Robots may now get information and updates from these systems in real time and act responsibly as a result of this integration.
If we want to make the most of these mobile robots, we need to make sure they're properly and completely integrated.
In addition to being necessary for order fulfillment, inventory management, and billing automation, AMR integration with ERP systems is also crucial.
With all of the systems working together, you can keep your customers up to current on their orders, stock levels, and expected delivery dates in real time.
Integrating AMRs with WMS systems is particularly crucial since it provides instantaneous data on inventory levels, such as where items are and whether or not they are available for purchase.
The integration of AMRs with ERP systems is also essential as it helps to automate various business processes, such as order fulfillment, inventory management and even billing.
Robots' ability to navigate, make decisions, and perform predictive maintenance is enhanced by the incorporation of IoT devices including sensors, cameras, and monitoring systems.
Ability to interact with human-involved processes
AMRs need to be able to engage with processes that include humans, in addition to interacting with other systems.
AMRs can't operate safely in a dynamic environment where people might be walking around and getting in the way unless they have the ability to identify and avoid obstacles.
Obstacle avoidance capacity is one of the main difference between agv and amr.
The ability of AMRs to engage with human-involved processes is greatly facilitated by the use of tailored human-machine interfaces (HMIs).
The flexibility of these interfaces makes it possible to design unique user experiences for each automated task.
The ability to use a hybrid automation model, in which robot’s tasks are generated on demand by people, is a common customisation.
A human worker, for instance, may require a specific tool or component in a manufacturing setting. An AMR can be sent to retrieve the requested tool or component after the worker has requested it by touch screen or voice command.
By coordinating their actions, humans and robots can work together more effectively and efficiently.
In addition, AMRs and human-involved processes that rely on effective interaction require the use of specialized task management systems.
This technology permits the robots and human workers to coordinate and get real-time updates on the progress of jobs.
A safer workplace is another benefit of human-robot collaboration. Accidents can be avoided by using safety measures like programming robots to stop when human workers are around.
To make sure that final goods are up to par, quality control tests can be done using human and robot collaboration.
Heterogeneous AMR fleet operations
Standardization and interoperability of communication protocols are essential for the efficient operation and orchestration of heterogeneous fleets, or for AMRs manufactured by various companies to interact and coordinate with one another.
Implementing traffic control at intersections, charging stations, pick-up and drop-off zones, doorways, and hallways is essential for the smooth operation of a fleet of AMRs from different manufacturers.
This can be accomplished by giving AMRs exclusive access to high-risk areas like pick, drop, scan, entry/exit points.
Because of this, AMRs must broadcast their locations and submit requests for exclusive access to specific areas and specific duties. By enforcing , we can reduce the likelihood of traffic jams or collisions and maximize fleet productivity.
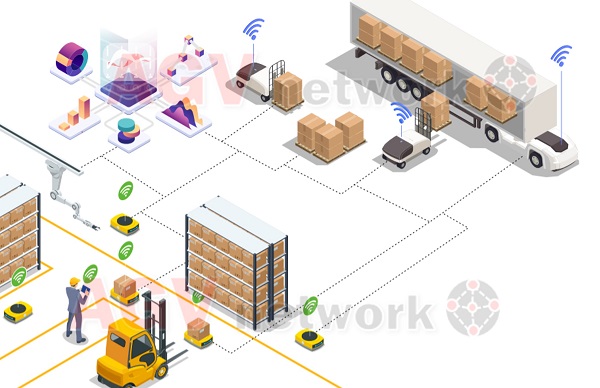
For this reason, the AGV/AMR community should pay close attention to this issue.
Customers will want to manage and orchestrate a wide variety of vehicles (including automated forklifts, security robots, floor scrubbers, and more) from a single interface.
???? It makes sense. Isn’t?
To ensure AMR compatibility, protocols are necessary.
Communication protocol interoperability is also crucial for smooth and efficient functioning.
This enables the robots to communicate with one another regarding things like where they are and how far along they are in their assigned tasks, leading to more efficient collaboration and utilization of available means.
Robot Operating System (ROS) is an example of open-source software that can be used to accomplish this goal, as it provides a standardized platform for creating robotic application software, which in turn facilitates cost savings and simpler integration.
The protocols used for communication across AMRs should range from REST API to VDA5050 to ZeroMQ to DDS to OPC-UA. Because of this, robots of different makes and models can work together efficiently.
What are the most common mobile robot communication protocols?
REST API
One common method of transferring information between computers is the REST API.
It's an easy-to-use protocol that can be adapted to fit into a variety of existing infrastructures. By integrating with WMS systems via REST APIs, AMRs can get up-to-the-minute data on stock, orders, and other metrics.
VDA5050
The automotive sector has its own dedicated communication standard called VDA5050 standard.
It offers a standardized means for cars to talk to other systems like warehouse management systems and enterprise resource planning systems. Due to the protocol's high security and dependability, it is well suited for use by AMRs in sensitive settings like hospitals, labs, and factories.
ZeroMQ
Data may be transferred between AMRs and other systems quickly and easily with the use of ZeroMQ, a lightweight and efficient messaging protocol. It's an easy and versatile way for AMRs to talk to outside gadgets like WMS and ERP programs.
Data Distribution Service (DDS)
Data Distribution Service, or DDS, is a protocol for exchanging information in real time over high-speed networks. It's great for AMRs that need to share lots of data at once, like video and sensor readings, in real time.
OPC-UA
In the realm of industrial automation, OPC-UA (Open Platform Communications - Unified Architecture) is the de facto standard for data exchange. It's a safe and dependable channel for AMRs to share information and data with other programs like WMS and ERP.
Conclusions
Rather than being a passive intermediary in the production process, AMRs are now integral parts of it.
In order to be successful in the market, mobile robots need to be interoperable with one another and be able to work together in a fleet that consists of a variety of different types of robots.
To facilitate productive interaction between AMRs and human workers and to ensure the efficient operation of a fleet of heterogeneous robots, it is necessary to have components such as customized human-machine interfaces, customized task management systems, object detection and avoidance capabilities, and support for multiple communication protocols.
Welcome to the new era of mobile robots.
|
Related articles
AMR Forklift : The Future of material handling
|
 Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Follow me on LinkedIn... let's create a mobile robot community to discuss and learn about these outstanding systems.