AGV Navigation: Methods, Comparison, Pros and Cons - Illustrated Guide
 What is the best navigation system for an AGV? Laser, natural, or magnetic? None. It depends on your project and your needs.
What is the best navigation system for an AGV? Laser, natural, or magnetic? None. It depends on your project and your needs.
What are the main AGV and AMR Robots navigation systems? In this article I explain how do AGV and AMR Robots navigate, and the advantages and disadvantages of each navigation method.
 My name is Alfredo Pastor, I have installed many mobile robots with different navigation methods. I have tested all of them.
My name is Alfredo Pastor, I have installed many mobile robots with different navigation methods. I have tested all of them.
And you know what? There is not a BEST navigation solution. Each project is different, your requirements are different, so there will be a best navigation for your specific needs. That said, let's see the different options.
This post is based on my experience. Please let me know if you agree or disagree.
Let's start with some humor... 😉
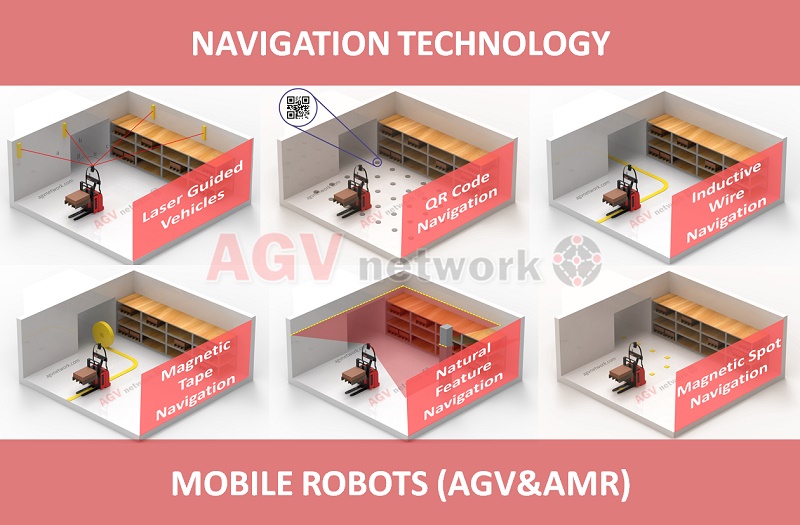
What are the types of AGV Navigation Systems?
The main AGV Navigation Methods are:
- Laser Guided Navigation
- Magnetic Navigation
- Magnetic spot navigation
- Inductive wire navigation
- Optical navigation, optic navigation.
- If we talk about Autonomous Mobile Robots, they navigate thanks to Natural Feature or Free navigation, including SLAM Navigation with LiDAR Sensors or camera based visual navigation systems.

Regardless the type of automated guided vehicle (forklift, tow tractor, cart, etc), the self-driving robot requires an Automated Guidance System able to localize, drive the AGV and inform the AGV Management System about the robot positioning.
AGVs navigate thanks to accurate, reliable and cost-effective agv navigation sensors and software. Depending on the application, AGVs and AMRs navigate thanks to 2D or 3D LiDAR, magnetic sensors, ultrasonic sensors, cameras, etc.
This Kollmorgen's one-minute video provides a concise summary of various technologies. However, I recommend reading further to gain a better knowledge of the available possibilities.
Before going ahead, let's explain that there are differences between Automated guided vehicles - AGVs and Autonomous Mobile Robots -AMR.
- AGVs follow a defined path, virtual or physical with external references. AGVs perform laser navigation, magnetic tape navigation, QR code navigation, etc.

- AMRs instead are not bonded to a given path and do not require any external reference to navigate. They navigate "watching" the environment, walls, columns, etc. They used what we call Natural or Free Navigation.

This topic is complex and creates many opinions in the industry. If you wish to know more, just download the agvnetwork's dedicated whitepaper (note: I do not advocate for a given technology, so I provide my "subjective" and personal opinion).
Let's see if you agree or disagree with me.

| Click here to download the whitepaper |
Let's have a first overview of the pros and cons summary of these technologies that I'll explain into detail in the following lines.
Summary: Advantages and disadvantages of mobile robots navigation systems? - AGV Navigation methods Pros and Cons

Choosing the right driverless guidance technology is essential because it will influence the overall performance of the Automated Guided Vehicle System
You should select the technique of navigation that best matches your needs rather than the most cutting-edge technology available. I have seen several initiatives fail due of a bad navigation choice.
What do you need?
✅ Accuracy?
✅ Reliability?
✅ Flexibility?
✅Low cost solution?
This table summarizes some benefits and drawbacks of each self-driving navigation technology.
| Navigation Tech | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
 | Easy to install. No invasive installation. Accurate positioning. High speed No costs due installation maintenance | Modifications require supplier intervention AGVs with this technology are expensive |
 | Easy to install. Easy to modify No invasive installation Accurate positioning. Reliable navigation AGVs with this technology are less expensive | Magnetic tape maintenance. Magnetic tape cost Not suitable for complex paths |
 | Easy to install Flexibility: Easy to add new paths or modify existing ones Low cost of installation No invasive installation. No costs due to implementation maintenance | Lower reliability in chaotic and variable environments Highly effective and efficient free navigation is still very expensive. Lower positioning accuracy compared with other navigation methods |
 | Free environment Accurate positioning. No costs due to implementation maintenance | Installation is easy but it still is more complex than magnetic tape Magnetic tape installation is faster and easier to modify |
Very important... 🙋🏼♂️ Please share this article if you find it helpful!
| In my opinion, there is not a "best" navigation system. It depends on your specific requirements. |
So let's discover out how does an Automated Guided Vehicle navigate!
How do Automated Guided Vehicles Navigate?
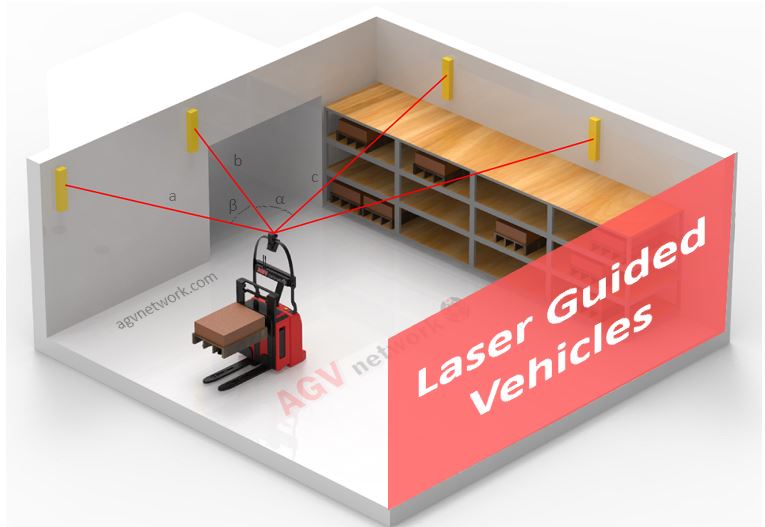
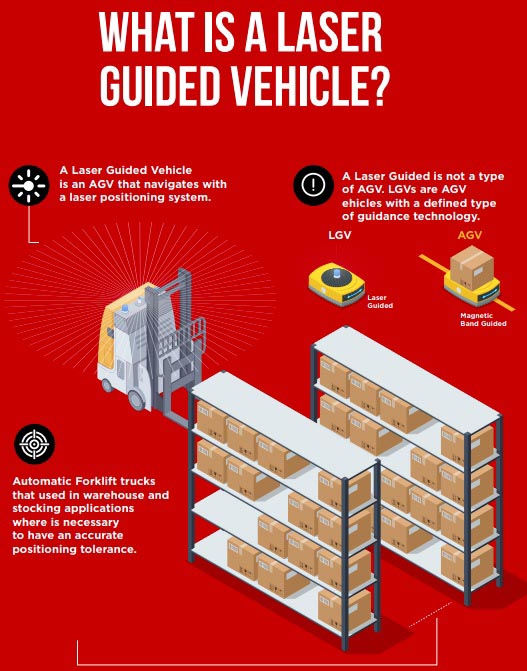
Laser Guided Navigation (LGV)
A LGV or Laser Guided Vehicle is an AGV that utilizes a laser positioning technology for navigation. Laser Navigation is one of the most popular navigation systems widely used in automated forklifts due to its realiability and accuracy.
Although LGVs are increasingly being replaced by more advanced natural navigation systems, allow me to begin by explaining what LGVs are.
In the following lines I explain how does an LGV work, but honestly... this video explains it much better than me:
What is the difference between AGV and LGV?
There is no difference because a LGV is an AGV with Laser Navigation. Thus, LGVs are a specific type of AGV.
What Types of AGV perform Laser Guided Navigation?
Laser navigation is widely used by Automatic Forklift trucks, used in warehouse and stocking applications thanks to its tight accuracy and reliability.
How does Laser Guided AGV work?
Each LGV is equipped with a Navigation Laser (simply called a Navigation Device) positioned on top of a pole that interacts with targets positioned in the working area.

The Navigation Device emits laser arrays in a full 360-degree pattern, which subsequently reach multiple reflector targets, such as tapes or cylinders. These reflectors then bounce the laser array signal back to the AGV Laser Navigation Device.
To determine their precise position, LGVs (Laser-Guided Vehicles) need to collect a minimum of three of these array feedbacks, which is achieved through a process known as triangulation. This calculation relies on highly intricate algorithms.
Depending on the specific AGV manufacturer, LGVs perform positioning calculations and adjustments at a remarkable rate, typically between 30 to 40 times per second. This level of precision makes these devices exceptionally accurate.

Flat and cylindrical reflectors. Which one is better? Discover more here.
When is it useful to choose a Vehicle with Laser-Guided Navigation?
When you require a high-speed vehicle with precise stopping capabilities and have multiple destinations and routes to consider, Laser-Guided Navigation is a convenient choice.
The installation process for Laser-Guided Navigation is straightforward. The AGV supplier takes care of installing all the necessary reflectors and then simulates the AGV's path on the AGV Management System to define the specific routes your AGVs need to follow.
One of the key advantages of this system is that it operates virtually, without the need for fixed infrastructures like tapes on the floor or wires beneath the surface. In the same corridor, you can create as many virtual routes as necessary to accommodate your project's complexity.
Therefore, if your project involves a large and intricate route system, opting for Laser-Navigation Vehicles proves to be an efficient and effective solution.
|
Navigation Technology |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Laser Guided Navigation
|
Easy to install. No invasive installation. Accurate positioning. High speed No costs due installation maintenance |
Modifications require supplier intervention AGVs with this technology are expensive |
What are some advantages to LGVs?
✅ LGV technology is easy to deploy. Installation is relatively fast. A big part of the job is done in an office by the supplier engineers.
✅ No intrusive installation. LGVs only require placing reflectors around the facility. These reflectors are easy to place, they can be adeshive tapes or just two bolts fixing. They are places at around 8 ft (2,5 m) height so once installed they will not interfere with the operations of the premises.
✅ Accurate tolerance positioning. Positioning algorithms are very sophisticated allowing a position accuracy close to ± 0,2’’ (5 mm). Laser Guided technology is the main option for stacking or racking operations in high warehouses.
✅ The vehicles performing laser navigation (so LGVs) are very efficient achieving up to 2 m/sec (6,5 ft/sec).
✅ No costs due to installation maintenance. The reflectors needed for navigating are passive, they do suffer wear and unless you do not break them they will not have any problem. It is only necessary to keep them clean and verify that they have not move for some reason.
What are some disadvantages of Laser Guided Navigation?
❌The AGV paths are easy to modify… but only by the supplier engineers. Any time you wish to update a path, to add new missions, to modify picking and dropping positions... you have to call your supplier.
❌ LGV Vehicles tend to be expensive. The vehicles including this technology have complex board controls and efficient navigation devices that make the average price of LGVs quite expensive.
❌Due to the fact that a vehicle's laser is typically situated on top to maximize the number of wall-based targets it can 'see', laser triangulation is not suitable for undercart or platform robots.
Magnetic Tape Navigation AGVs
In this case, automated guided vehicles are equipped with magnetic sensors and follow a defined path made by a magnetic tape track.
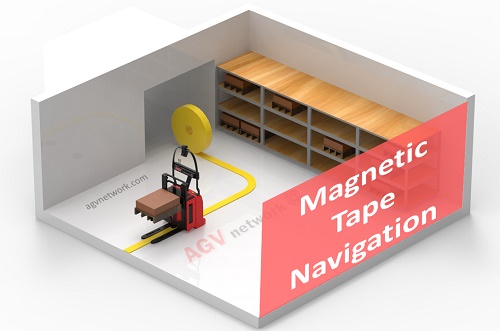
Watch the following video to understand how do magnetic guided vehicles work:
The guided route is made by a magnetic tape that is placed on the floor surface.
A magnetic sensor on the AGV detects the magnetic field from the tape and drives the AGV following the path.
Magnetic Tape is easy to install. High-bond adhesive is used for laying the magnetic tracks. Standard dimensions are 1 mm thick and 5 cm wide, so the tape isn’t invasive at all.

The AGV management system can indicate to the AGVS how and where to drive using tags (rfids) or magnetic indicators placed on the floor.
At these predetermined positions, the AGV can decide what to do: turn left, stop, engage a trolley, etc.
When is useful to choose an Automated Vehicle with Magnetic Navigation?
Magnetic navigation is primary preferred for Automatic Guided Carts (AGC) Magnetic Navigation accurary allows low-profile AGVS to engage trolleys from below.
Something like this:
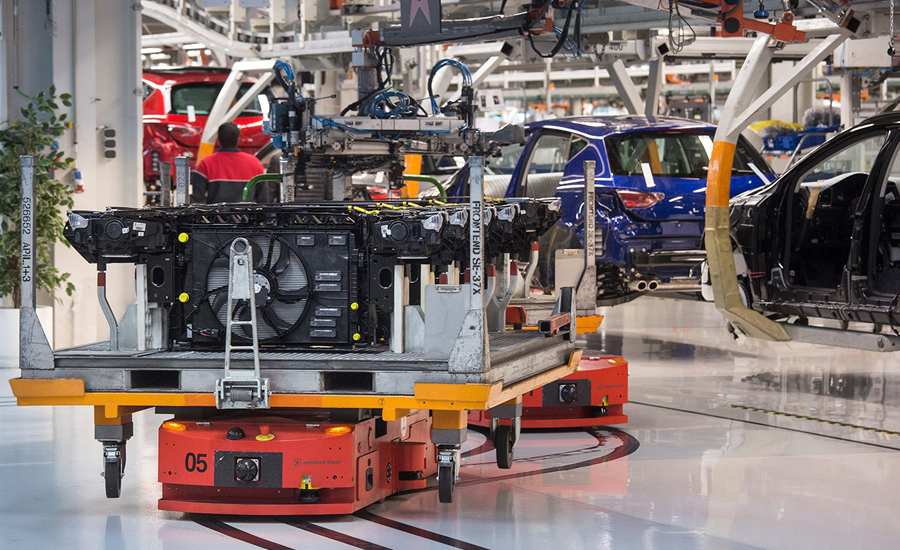

Image from SEAT Martorell (Spain)
Magnetic Navigation is mainly suited for well-defined routes without lots of routing options.
|
Navigation Technology |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Magnetic Tape Navigation
|
Easy to install. Easy to modify No invasive installation Accurate positioning. Reliable navigation AGVs with this technology are less expensive |
Magnetic tape maintenance. Magnetic tape cost Not suitable for complex paths
|
What are some advantages to Magnetic Tape Navigation?
✅ Easy to install: Installation is easy, it doesn't require any high skill professionals. Low cost workforce.
I know that AMR suppliers and Natural Navigation technology suppliers state that installing magnetic tape is time consuming... well, I have installed hundreds of magentic AGVs and I can tell that you can install more than 500 m in just one shift.
Anyway, it's true that if the project is complex with many curves and pick and drop positions, natural navigation is much more convenient and faster to deploy.
✅ Easy to modify: The end user can modify routes simply by placing or removing the adhesive magnetic tape from the floor.
✅ No invasive installation: The installation of the magnetic tape doesn’t require any infrastructure changes or modification either before or after the placement of the tape. Magnetic tape can be installed without stopping customer operations.
✅ AGVs have highly accurate positioning: Positioning tolerance is very precise allowing accuracy close to ± 2 mm (0.07 inch).
✅ Reliable navigation: Strong and reliable navigation that does not suffer from dust, noise, or dirtiness. It does not depend on the surrounding environment.
✅ Well-established technology : AGVs with this navigation technology are less expensive and highly effective.
What are some disadvantages to Magnetic Tape Navigation?
❌ Magnetic tape maintenance: Magnetic tape, paint, and tags/codes are all susceptible to deterioration over time, which can lead to "broken" routes and vehicle faults. It could be necessary to embed the tape on the floor or cover it with an epoxy resin or dedicated protective tapes that would increase the installation cost.
❌ Magnetic tape cost: For big installations with a long tracks , magnetic tape costs will increase installation costs.
❌ Installing long tracks and and crosses on the floor is time consuming (so expensive) and complicates AGV traffic management.
Natural Navigation AGV - Free Navigation
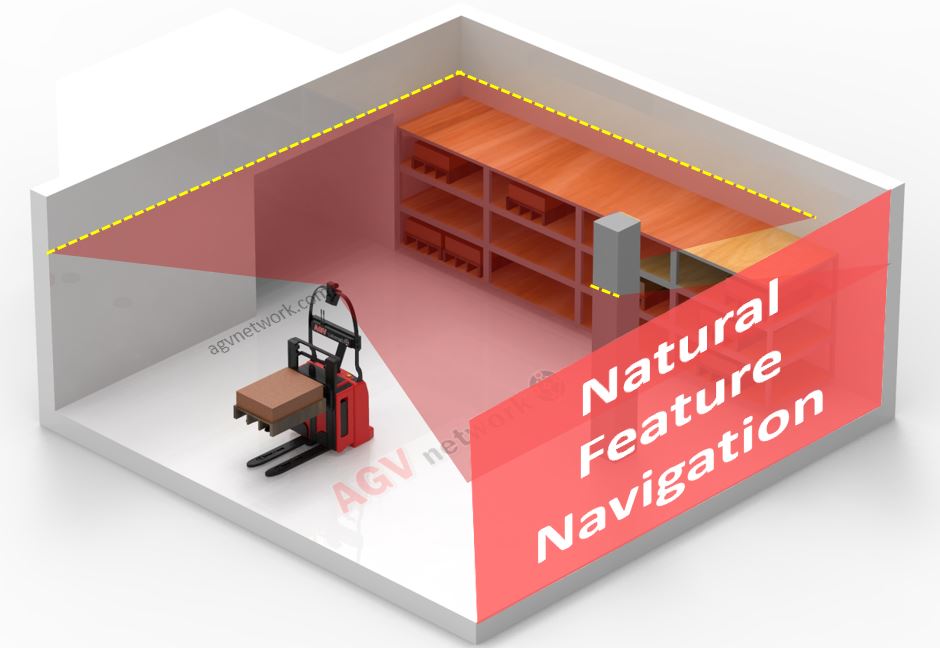
There are several technologies included in what’s called “Natural Navigation”. As anticipated, mobile robots performing some type of "natural" or "free" navigation are typically classified under the "AUTONOMOUS" umbrella.
Mobile robots performing natural or free navigation are known as "Autonomous Mobile Robots - AMR"
The most important free technology is the SLAM Navigation, or Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM).
It means that an AGV with SLAM Navigation is able to map its environment and localize where it is thanks to the information received from the surrounding environment.
The mobile robots are able to map the environment with different sensors such vision cameras, lidar sensors or even with the same lasers used for safety purposes.... all of this info is combined with internal inertial measurement unit (IMU) to define and recalculate the real AGV positioning.
All these calculations are made by a highly complex algorithms called SLAM... So, SLAM is more of a concept than a real technology.
| 🙋🏼♂️ My advise: There is not a best natural navigation technology... there will be a best supplier with a good navigation technology. |

How do AGVs with SLAM Navigation work?
Mobile robots that utilize natural navigation, commonly referred to as Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), operate by mapping their surroundings. This method, known as Natural or Free Navigation, allows AMRs to navigate and orient themselves within an environment without relying on tapes or reflectors, essentially by "observing" their surroundings.
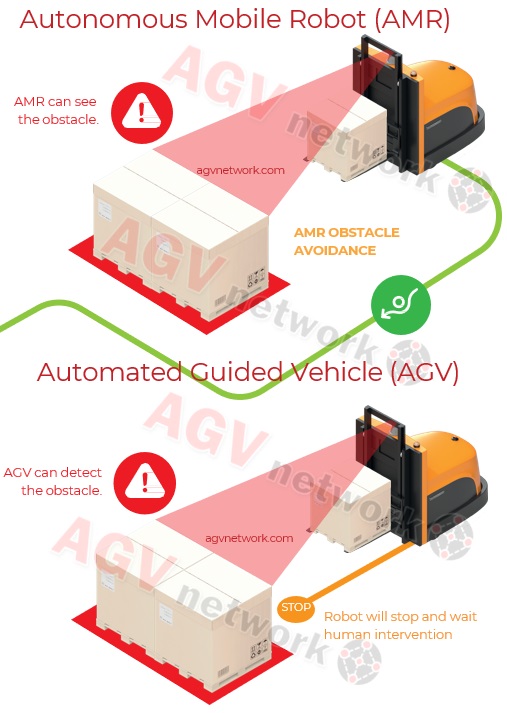
Moreover, AMRs possess the ability to spontaneously redefine their routes and circumvent obstacles. They are not constrained to predefined paths and can adapt their trajectory as needed. When encountering an obstruction, an AMR is designed to adjust its path to bypass it.
When is it useful to choose AGVs with natural navigation?
SLAM Natural Navigation is step by step improving and will substitute for other kinds of navigation such magnetic navigation, optical navigation ,etc. Well... this is my opinion.
It’s a good solution for Automated Pallet Jacks, AGCs and Tugger AGVs. Many of the main Top AGV Manufacturers are developing and including this technology on their "ex" AGVs.
The main concern about Natural (SLAM, LIDAR, etc) technology is its reliability in variable and chaotic environments such as production lines where there’s continuously moving of people, items, boxes, pallets, etc.
In these conditions the AMR might not be able to LOCALIZE where it is. In this cases, we still need to install some reflector or QR code to provide a more accurate reference to the robot.
For this reason, SLAM with LiDAR is a great solution for mobile robots where you have well defined profiles and environments with fixed structures such as walls and columns.
Natural Navigation is typically used for warehouse robots and hospital robots… in general, in any environment with a low or limited level of “confusion”.
| This said, it is important to understand that natural navigation systems are improving and are able to work in more and more complex environments. |
If you wisht to have more in-depth technical details about SLAM technology and Natural Navigation AGVs, check out this article: Natural Navigation Automated Guided Vehicles where I go deeper into the "magic" world of the natural navigation technology.
|
Navigation Technology |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Natural Navigation
|
Easy to install Flexibility: Easy to add new paths or modify existing ones Low cost of installation No invasive installation. No costs due to implementation maintenance |
Reliability in chaotic and variable environments Highly effective and efficient free navigation is still very expensive. Lower positioning accuracy compared with other navigation methods |
What are the benefits of Natural Feature Navigation?
✅ It’s the future: More and more companies are investing, developing and improving Natural Navigation Technology.
✅ Easy to install: Just draw a line in your pc or drive your robot to teach the track. It will map and localize it by itself and it will do the rest of the job.
✅Easy to modify. Same as the installation, just add, remove, modify the tracks or destinations effortless.
✅ Low installation costs. Installation is fast and easy.
✅ No invasive installation. Natural Navigation AGVs do not require any kind of external infrastructure that could interfere with plant operations.
✅ No costs due to implementation maintenance. There is nothing installed for the navigation, so there is nothing to maintain.
What are the drawbacks of Natural Feature Navigation?
❌ Navigation Reliability. Autonomous Mobile Robots with Natural Navigation could have “orientation” problems in industrial and/or confusing areas due to the variable environment. In other words, if the environment is too chaotic, the robot could not understand where it is.
❌ Vehicles with good and reliable natural navigation are still more expensive if compared to other technologies.
❌ Lower positioning accuracy compared with other navigation methods.
Magnetic Spots Navigation

What is AGV magnetic spot navigation?
AGVs can navigate following small cylindrical magnetic spots embedded on the floor. Magnetic spots are commonly cylindrical magnets with dimensions close 20x10 mm (0,8x04 inch).

Magnetic spots and AGV sensor. Image from AMERDEN AGVs
Magnetic spots are installed every 250-500 mm (near 15 feet) creating a virtual path.
The AGVs goes from one spot to the next using sensors and controls such hall-effect sensors, encoders, counters, gyro sensor and other kinds of encoders to calibrate against steering angle errors.
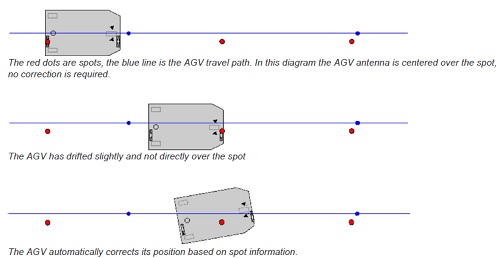
AGVs follow a CAD drawing previously loaded on the AGV Management System while the magnetic spots provide a reference in accordance with the map.
Positioning tolerances are relatively good achieving near 2,5 mm (1’’). This tolerance is better than tolerances obtained by other “free” navigation systems such SLAM, LiDAR, etc.
Installation is quite easy. A small hole on floor is required where the magnet is positioned. After that installation, hole is covered by epoxy resin.
|
Navigation Technology |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Magnetic Spot
|
Free environment Accurate positioning. No costs due to implementation maintenance |
Installation is easy but it still is more complex than magnetic tape Magnetic tape installation is faster and easier to modify
|
What are the pros of Magnetic Spots Navigation?
✅ Once installed, there aren't any structures on the floor. It seems to be “free.”
✅ Accurate positioning. Positioning algorithms are very sophisticated, allowing an accuracy position close to ± 2,5 mm (0.1 inch).
✅ No maintenance costs. Once installed, there is no need for any kind of maintenance because there is no path wear.
What are the cons of Magnetic Spots Navigation?
❌ Installation is not so complicated but it still is more complex than magnetic tape.
❌ Installation is quite invasive beacuse it is necessary to make holes. There will be noise and dust,
❌ It is complicated to modify paths, add new destinations, etc.
AGV Robots Navigation Benchmark Comparison
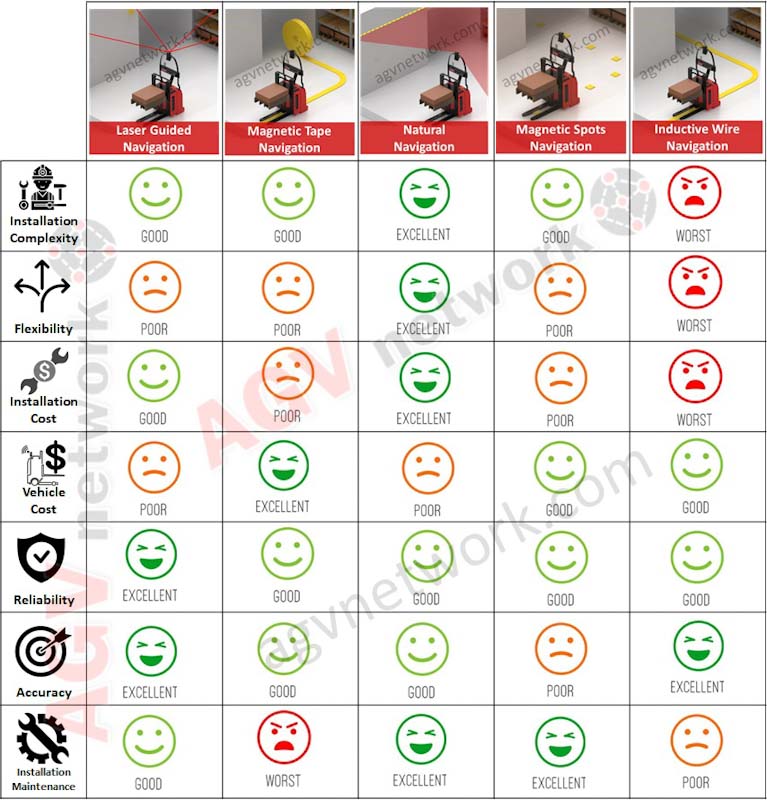
The following table ranks different AGV Navigation technology based on different variables:
✅ Installation complexity: Is it easy to install? Is this technology intrusive? Does it require civil works? Is it necessary to stop user operations while installing the mobile robots?
✅Flexibility: Is it easy to modify the mobile robot paths? Can the user add new picking or dropping positions? Is it easy to add new destinations or routes?
✅ Installation cost: Is the installation phase expensive?
✅ Vehicle cost: How does navigation technology influence AGVs or AMRs vehicle cost?
✅ Reliability: Is this navigation reliable? Does the vehicle lose the track?
✅ Accuracy: What is stopping tolerance? Is this technology accurate?
✅ Installation Maintenance: Once the system is intalled. Is it necessary to maintain the hardeware needed to navigate? Does wear or dust influence navigation performance?
Conclusion
When selecting the navigation method for a mobile robot project, it's crucial to prioritize the specific needs of your project over the allure of the latest technology.
Various navigation techniques, including magnetic, laser-guided (LGV), natural navigation, and Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), each have distinct advantages and limitations.
The effectiveness and cost-efficiency of your AGV system hinge on choosing the technology that best aligns with your operational requirements.
Opting for the most advanced or trendy solution may not always yield the best results if it doesn't suit your specific use case.
Additionally, partnering with the right supplier, one who understands your needs and offers suitable, reliable solutions, is just as important as the technology itself.
A well-matched navigation method and supplier can significantly enhance system performance and cost-effectiveness, ensuring a successful implementation of AGV technology in your operations.
 Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Follow me on LinkedIn... let's create a mobile robot community to discuss and learn about these outstanding systems.