How do Security Robots work?
 New affordable and powerful navigation, sensing, and communication technologies enable security robots to match and even outperform human guards. Let's discover how do security mobile robots work.
New affordable and powerful navigation, sensing, and communication technologies enable security robots to match and even outperform human guards. Let's discover how do security mobile robots work.
How do Security Robots work?
Security Robots are autonomous mobile robots that move across an environment collecting data in order to fulfill security tasks. Advanced sensors are used by security robots for localization, detection, and communication. Security robots can behave and respond in the presence of potentially dangerous scenarios thanks to powerful AI technology.
To make a security robots perform their security duties like a human guard, there are many technical challenges to be addressed.
They aren’t just cameras mounted to a wall, like standard security systems. These autonomous robots have the added advantage of movement and direct interaction with the surrounding environment.
The main technical obstcles are:
Robot navigation (how do robots travel autonomously?)
Data collection (what devices are used to capture video and pictures?)
Communication (how is information transferred to the management system?)
Data management (how does a robot’s software manage information?)
Luckily, autonomous technology has evolved rapidly, and it is now possible to build robots to meet people’s security needs.
How do Security Robots navigate and patrol?
Autonomous Security Robots navigate by combining different advanced technologies such satellite GPS localization, contour-based natural navigation, visual navigation, or a combination of these systems.

Navigation is a key factor to consider, and itdepends on the specific working environment of the target patrol areas. ASRs can work indoor, outdoor, or both.
|
Check these articles: |
The area where the security robot works can also be an open area, which means that a GPS based navigation alone could work fine.
Nevertheless, it is common for these security robots to work in more complex and confined areas that include both indoor and outdoor locations. Patrols may start inside a building, travel through hallways and rooms, and extend to the perimeter of the building before returning to the start of the patrol cycle.
An integrated solution includes both GPS and contour-based natural navigation with LiDAR instruments which enables robots to find their way around a patrol area and avoid obstacles. This means that a robot will travel a predefined path to precision but can avoid a box or person in their way. It won’t hit a wall and fail to operate like a child’s toy car.
ASRs can also navigate via visual navigation, but in this case, it is necessary to have sufficient illumination. Lacking sufficient light, the robots can use infrared (IR) illumination,invisible to humans, but highly useful to the robot in darkness.
Behind the hardware, the control algorithms, such as the SLAM technique, enable the robots to patrol in predefined routes, or with the application of Artificial Intelligence algorithms, they enable them to run autonomous patrols.
These are some of the key skills that every ASR navigation system should have:
Reliable autonomous natural navigation technology
Obstacle avoidance feature
Ability to navigate in low light conditions
Patrol routes must be easy to deploy and modify
Self-navigation to charging station when needed
How do Security Robots perform surveillance and data collection?
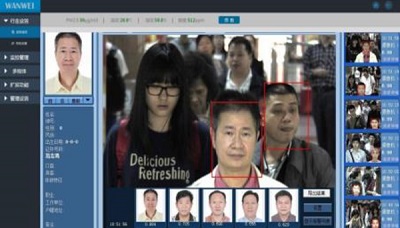
Security robots must be able to identify and detect objects of interest, such as people and vehicles. In this sense, visibility is another key problem to tackle.

ASRs count on different devices to scan their surroundings, capture video data for surveillance, object and individual detection and identification, forensic investigation, and real-time situational awareness.
Anything that a human would have to do, the robot must also do if the robot will assist the human patrol with the same surveillance efficiency.
Robots can record and/or be used as live cameras for security control centers.
Panoramic 360-degree high-definition cameras

ASRs count on 360-degree cameras where a view in every direction is recorded at the same time.
PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom)
A pan–tilt–zoom camera (PTZ camera) is an IP where the user can control the movement and position of the lens from a remote location using controls on an Internet browser or software application. Home security systems use a similar technology that allows the homeowner to view their camera’s sight via a smart phone.
Panning refers to horizontal movement of the lens where tilting describes vertical movement. If a person or car is moving, panning and tilting allows for constant tracking and monitoring when the robot is fixed in place.

This feature gives the opportunity to zoom in to fragments of the environment or to scan the entire area during continuous rotation.
If a person is detected, robots can stop the 360° camera rotation, zoom, and get a photo for facial recognition.
Low-light infrared cameras
The robots can have visibility in the dark, which tends to be difficult for human guards. This can save on costs of electric lights and can keep sensitive locations dark as needed.
What happens if the electricity is cut or if a power line goes down during a storm? It is very important to have surveillance cameras continue working properly during all types of light conditions.
These cameras with Infrared (IR) LEDs illuminate the surrounding area via invisible infrared light shifting from color image to black-and-white image.
Generally, natural light allows for color image capture, while IR cameras can only capture black and white images. However, the quality of the image isn’t lost as compared to natural light cameras.
Thermal cameras
Equipped with thermal cameras, these robots can detect thermal properties and capture heat signatures of people, animals, or vehicles, as well as gas leaks, through smoke, fog, or other obstacles.
We have all probably seen the military application of thermal imagery. Even in the commercial application, it is highly powerful in its ability to see “through” objects and capture the heat signature of a target object on the other side of a barrier.

How do ASRs communicate with to the management center?
One of the most interesting capability of security robots is the application of continuous streaming video recording and transferring to a management center or cloud. Cloud storage allows off offsite storage and monitoring from any location that the operator needs to be.

Further, because the data is digitally gathered and delivered to the storage center, multiple users could access the data stream or historical video from multiple locations.
If recorded video is sent to the control center in real time, officers in the control center can make security decisions more easily and promptly.
Thanks to the development of wireless communication technologies in recent decades, the robots can use 4G or Wi-Fi networks to deliver the video and other collected data for analysis.
Though closed capture cameras are common, autonomous robots are no longer bound by the cord and can maneuver with more freedom and flexibility.
Wi-Fi connections provide more data transfer capacity, but unfortunately, Wi-Fi is not always available or is much weaker in outdoor or remote applications.
In these cases, robots could be equipped with on-board autonomous intelligent video surveillance system and human recognition.
In a sense, when communications are cut due to poor signal strength, the robots can act as self-contained monitoring units that can act as the human interpreter of the images, until it can reconnect with the monitoring servers.
Whenever required, ASRs under 4G can transfer photo and video files or simply transmit alarm messages to the security control center, or guard smartphone.
In this case, the data traffic generated by the robot is small, so the robot deployment does not require additional investment in a robust and reliable Wi-Fi network.
Of course, as soon as 5G networks become more readily available, it will be possible to perform more video, audio, and data intensive streaming operations.
If Wi-Fi is available, ASRs work with a fixed IP address and can be considered a mobile part of video surveillance systems.
In this case, robots can send a huge amount of data in real-time for continuous surveillance.
It is also possible to combine both communication methodologies, 4G and WiFi.
If there’s good WiFi coverage, the robot can use the WiFi net. When the robot moves to an area with a poor or uncertain Wi-Fi signal, it can automatically switch to a set 4G system.

Besides the hardware capability to get video and pictures, it is necessary to have a system able to manage all the information and data.
CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) based image recognition algorithms enable the robots to do image recognition actions so that different targets like people, trees, cars, walls can be distinguished, identified, and tracked.
Follow this link for more in-depth information about this exciting technology.
Video analysis algorithms can even detect motion and forecast potential risks, which is especially useful for law enforcement in daily duty requirements.
Security managers will also be interested in collecting continuous video data and providing a complete audit trail for future review.
More features of Autonomous Security Robots
Two-way communication device
Robots can be programmed to broadcast messages related to security, safety, etc.
Messages can be done in several languages.
Security robots in some scenarios like corporate campuses or shopping malls might need to have 2-way communication capability.
ASRs count on microphones, speakers and call buttons and can be used to remotely speak with the security center.
Artificial Intelligence to boost security performance
With the backend AI algorithm analysis, the system can even identify suspicious sounds such as breaking glass and send an alert to the security network.
Sounding an audible siren or visible alarm (such as flashing a strobe) could be useful as a visual deterrent to trespassers.
How do mobile security robots recharge?
ASRs count on advanced lithium battery technology to operate under high operating demands for long periods of time.
An average patrol cycle lasts between 2 to 2.5 hours.
When the battery level gets low, the robot will autonomously reach at a charging station for opportunity charging without any kind of human intervention. This frees up the security officer to stay in the control center as they would not need to leave their post to plug in the robot.
ASRs need around 20 min to charge their battery and keep on working.
For larger open areas that may not be suitable to set up charge stations, solar panels directly attached to the robots exterior could be another option to provide robots more power, or at least a slightly longer operating time.
|
Related articles
Autonomous Last Mile Delivery Robots
Main Applications of Autonomous Mobile Robots
AGV Applications : Where are Automated Guided Vehicles Used?
Robots in Hospitals: Types, Applications and Advantages |

